

The presence of bed bugs can markedly disrupt your living environment, necessitating immediate and effective treatment strategies. Understanding the life cycle of these pests is vital, as it informs both DIY methods and the necessity for professional intervention.
From thorough vacuuming and high-temperature laundering to specialized chemical treatments, there are numerous approaches to reclaim your space.
However, the complexity of bed bug infestations raises important questions about prevention and long-term maintenance. What steps should one take to guarantee that these unwelcome guests do not return?
Bed bugs are often found in various environments, frequently infesting homes, hotels, and public transport due to their ability to hitch rides on clothing and luggage. These small, reddish-brown insects are adept at evading detection, often hiding in cracks, crevices, and upholstery.
Adult bed bugs measure approximately 4 to 5 millimeters in length and can survive for several months without feeding. Their primary food source is human blood, which they obtain through bites, typically occurring at night. The presence of bed bugs can lead to itchy welts and significant distress for affected individuals.
Understanding their life cycle, which includes eggs, nymphs, and adults, is vital for effective management and control. Awareness of these factors is essential in combating infestations effectively.
Numerous DIY treatment strategies can effectively address bed bug infestations, allowing homeowners to take proactive steps before seeking professional assistance. One of the most effective methods is to wash and dry bedding and clothing at high temperatures, as heat kills bed bugs and their eggs.
Vacuuming infested areas thoroughly, including seams and cracks, can help remove adult bugs and larvae. Additionally, sealing cracks and crevices with caulk prevents bed bugs from hiding or entering new spaces.
Utilizing diatomaceous earth, a natural insecticide, can also be an effective deterrent when applied in areas where bed bugs are suspected. Finally, using bed bug interceptors can help monitor and control the spread of these pests by trapping them before they reach your bed.
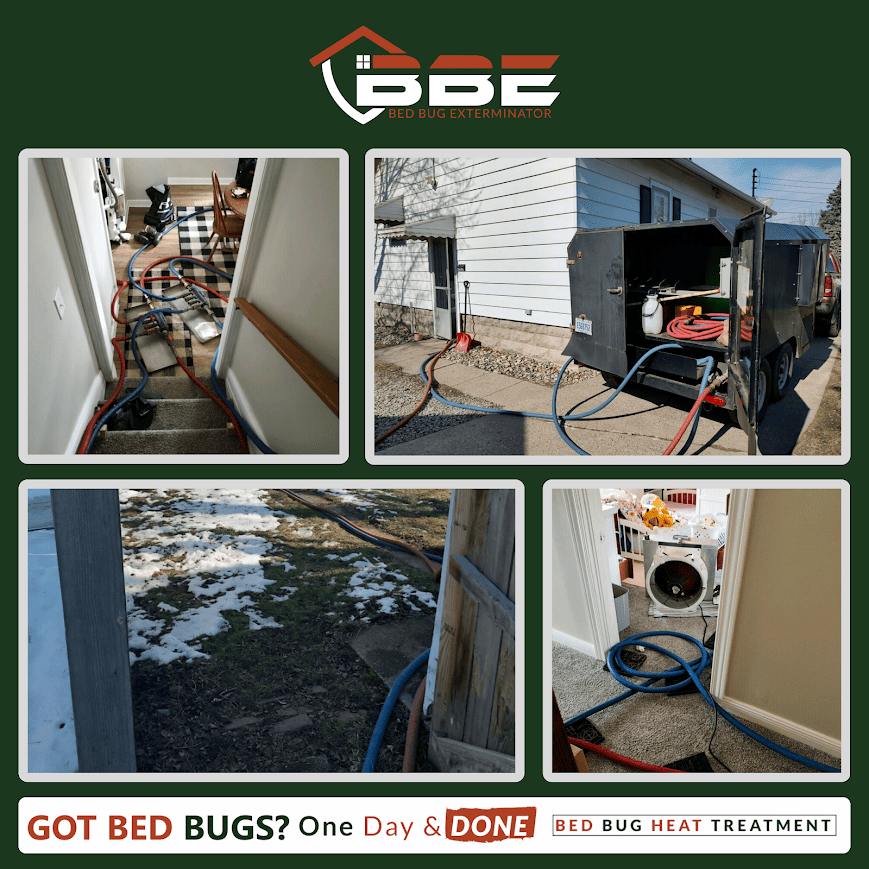
When DIY treatment strategies fall short in effectively eliminating a bed bug infestation, professional extermination options become necessary. These services employ trained technicians who utilize specialized equipment and techniques to guarantee thorough eradication.
Common methods include heat treatment, where the entire infested area is heated to lethal temperatures for bed bugs, and chemical treatments, which involve the application of insecticides specifically designed for bed bugs. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) approaches are also utilized, combining multiple strategies to minimize pesticide use while maximizing effectiveness.
Professionals conduct extensive inspections to identify hiding spots and assess the severity of the infestation. By leveraging their expertise and resources, professional exterminators can provide a more reliable solution, ultimately restoring comfort and safety to your living space.
Effective prevention strategies are essential for safeguarding your home against bed bug infestations. Begin by regularly inspecting your living spaces, particularly areas where you sleep and relax, for any signs of bed bugs, such as shed skins or dark spots.
When traveling, always examine hotel rooms and keep luggage off the floor. Utilize protective mattress and box spring encasements to deter bed bugs from settling in. Additionally, reduce clutter in your home to eliminate potential hiding spots.
Vacuum frequently, especially carpets and upholstery, and dispose of the vacuum bag immediately. If you acquire second-hand furniture, inspect it thoroughly before bringing it inside. By implementing these proactive measures, you can greatly reduce the risk of a bed bug invasion in your home.

After implementing prevention strategies, maintaining a bed bug-free environment is crucial following treatment. Regularly inspect your living space for signs of bed bug activity, such as shed skins or dark spots.
Vacuum frequently, focusing on areas where bed bugs are likely to hide, including seams of mattresses, upholstered furniture, and baseboards. Wash bedding and clothing in hot water weekly and dry on high heat to eliminate any potential eggs or bugs.
Encase mattresses and box springs with protective covers to prevent re-infestation. Additionally, minimize clutter, as it provides ideal hiding spots. Be vigilant during travel, inspecting hotel rooms and luggage. By adhering to these maintenance practices, you can guarantee your space remains bed bug-free and comfortable.
Recognizing the signs of a bed bug infestation early is essential, but there are instances when professional intervention becomes necessary. If you notice persistent bites despite DIY treatments, it indicates that the infestation has likely escalated beyond manageable levels.
In addition, if you encounter bed bugs in multiple rooms or find them in unusual locations, such as seams of furniture or electrical outlets, the situation warrants expert help. Professional pest control services possess advanced techniques and products that guarantee thorough eradication.
Moreover, if you have allergies or respiratory issues, seeking help promptly can mitigate health risks associated with bed bug exposure. Remember, timely intervention can save you time, money, and stress in the long run, restoring your home to a safe haven.

Bed bugs can survive without a host for varying lengths of time, typically ranging from several weeks to several months, depending on environmental conditions. In cooler temperatures, their metabolism slows, allowing them to endure longer periods without feeding. Conversely, higher temperatures can reduce their survival time. However, it is essential to note that prolonged periods without a host can weaken bed bugs, making them more susceptible to extermination efforts.
Bed bugs are known to be resilient pests, but extreme cold temperatures can greatly impact their survival. Research indicates that temperatures below 0�F (-18�C) can be lethal to bed bugs, particularly when maintained for several days. However, their eggs are more resistant, requiring prolonged exposure to freezing conditions to guarantee eradication. Consequently, while cold can inhibit bed bug populations, it is essential to apply consistent and thorough methods for effective control.
Bed bugs, scientifically known as Cimex lectularius, can survive without a host for varying durations depending on environmental conditions. Generally, they can live for about 2 to 6 months without feeding, though some individuals may endure up to a year under ideal conditions, such as cooler temperatures. Their ability to enter a state of dormancy allows them to withstand extended periods without a blood meal, complicating control and eradication efforts.